Gukesh D’s Groundbreaking Triumph: India’s New World Chess Champion
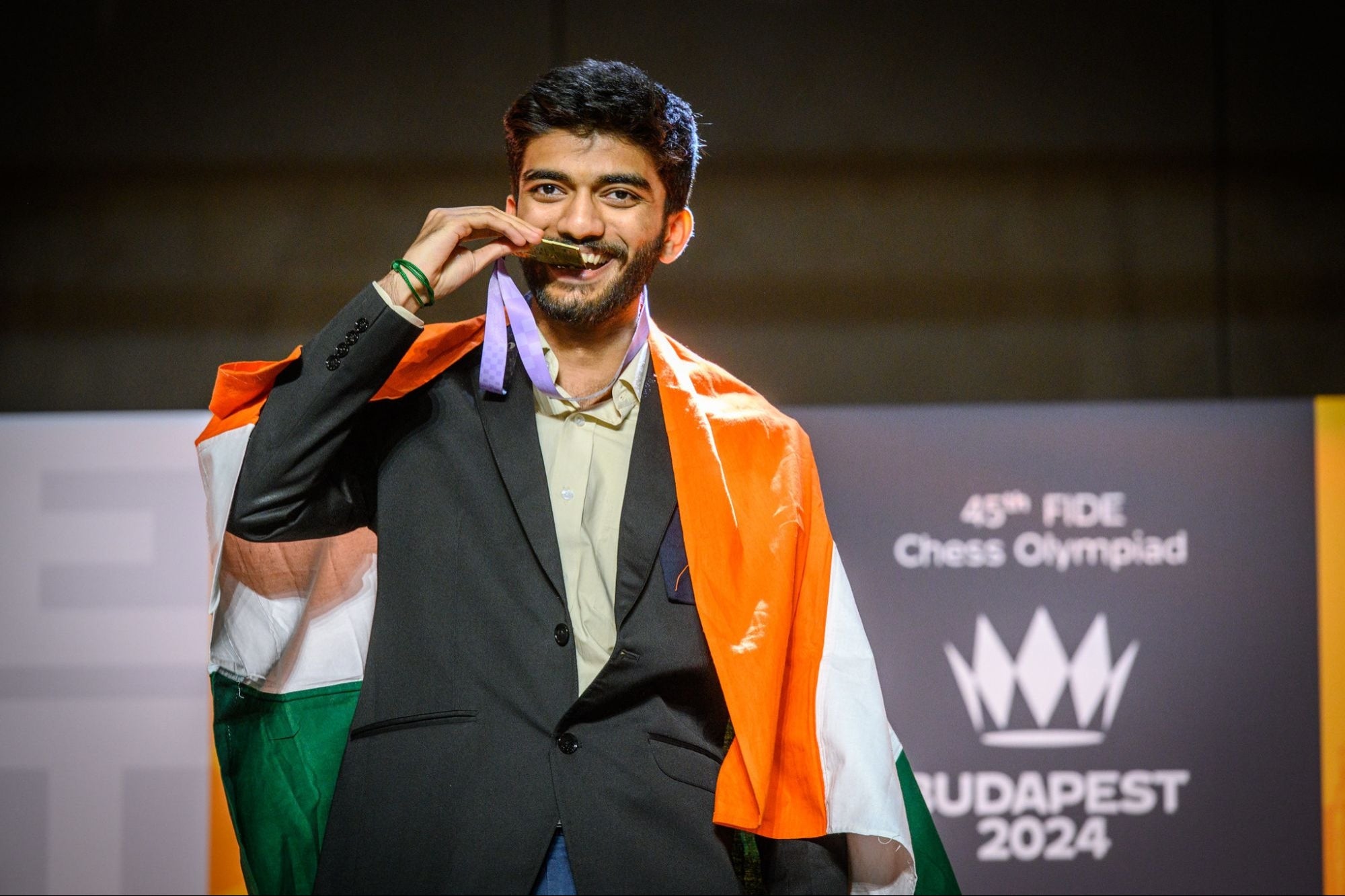
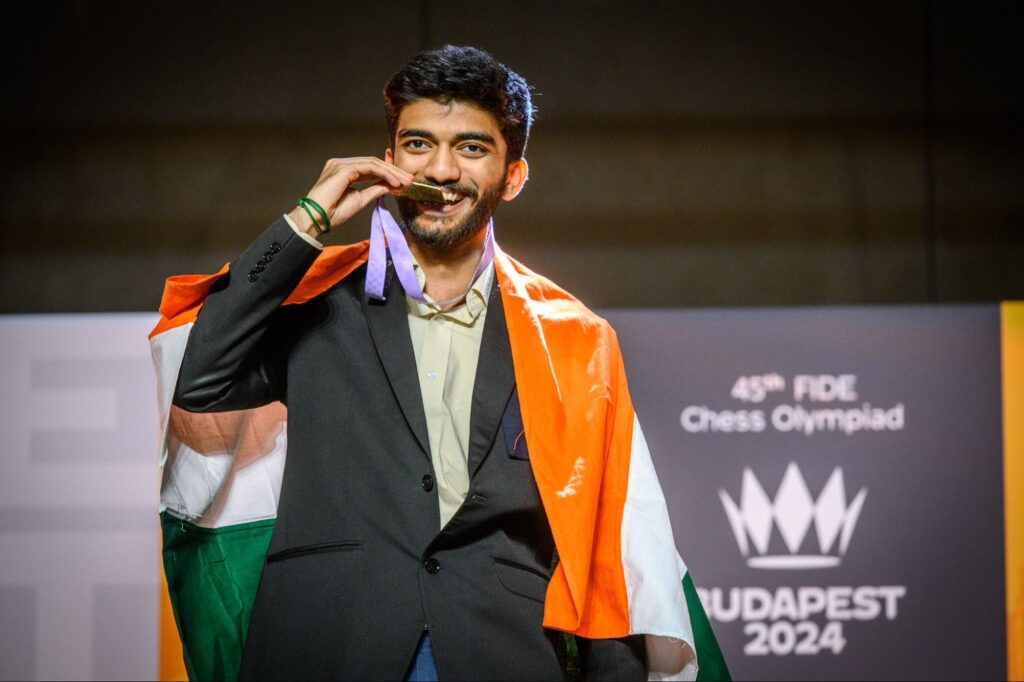


The world of chess has just witnessed a seismic shift with Gukesh D emerging as the World Chess Champion, making him one of the youngest and most talented players to ever claim the prestigious title. Gukesh’s triumph is not just a personal milestone but a moment that will be remembered for years to come. At the age of just 18, this young prodigy from India has captured the hearts of chess enthusiasts worldwide, carving out a legacy of his own.
His victory against one of the greatest players of the modern era, Magnus Carlsen, in the World Chess Championship has changed the trajectory of the game itself. Let’s dive into the incredible journey that led to this historic achievement.
The Rising Star: Gukesh’s Journey to Glory
Born in Chennai, India, in 2006, Gukesh D showed a natural aptitude for chess at a young age. By the time he was 10, his skills were already outshining those of many seasoned players, and it was clear he was destined for greatness. At the age of 12, he became the youngest Indian International Master and, just a few years later, at 15, he earned the title of Grandmaster.
What set Gukesh apart from his peers was not just his ability to memorize openings or execute well-known strategies. His playstyle was aggressive yet nuanced, blending deep preparation with creative, out-of-the-box thinking. As he ascended through the ranks, he began to take down top grandmasters, leaving the chess world in awe of his abilities. But winning the World Chess Championship, a title long dominated by a few select players, was always going to be a massive challenge.
The Epic Showdown: Gukesh vs. Carlsen
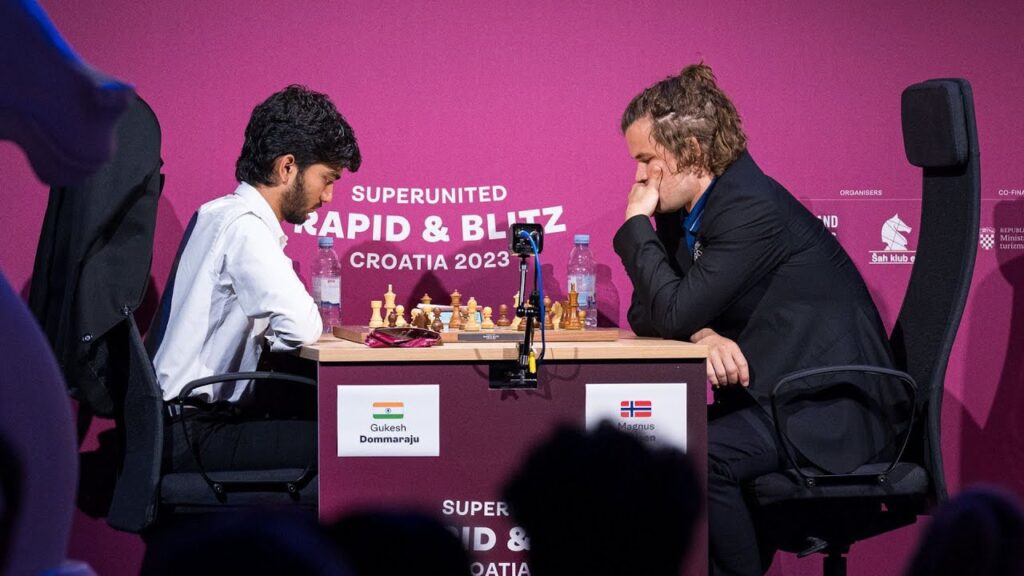

The World Chess Championship is the ultimate stage for any chess player. It’s where legends are made and dreams come true. For Gukesh, the road to the championship was long and arduous. Facing off against the reigning World Champion Magnus Carlsen, a player who had redefined chess for over a decade, seemed like an impossible task. Carlsen, with his strategic depth and unparalleled endgame prowess, was a formidable opponent for the young challenger.
However, Gukesh’s mindset was different. He was calm, focused, and determined not to be overwhelmed by the occasion. From the very first game of the match, it was clear that Gukesh wasn’t just a challenger—he was a contender. His preparation was impeccable, his moves were precise, and his ability to handle pressure was extraordinary.
In a series of dramatic games, Gukesh outplayed Carlsen, not by brute force but by his ability to navigate complex positions with subtlety. He wasn’t afraid to take risks, and his sacrifices were often calculated, forcing Carlsen into uncomfortable positions where he could no longer rely on his usual endgame supremacy.
By the time the final game concluded, Gukesh D had sealed his place in history. The chess world was in shock—India’s youngest World Chess Champion had arrived. He had beaten a giant, and the world would never look at chess the same way again.
A New Era for Chess
Gukesh’s victory is not just a personal achievement; it represents a larger shift in the world of chess. The global chess scene has traditionally been dominated by players from Europe and Russia, with legends like Bobby Fischer, Anatoly Karpov, Garry Kasparov, and Magnus Carlsen shaping the game’s history. However, Gukesh’s triumph is a testament to the globalization of chess, where players from all corners of the world, especially from India, are now emerging as top contenders.
For India, Gukesh’s win is especially significant. The country has long been a chess powerhouse, producing legends like Viswanathan Anand, but Gukesh’s victory marks a new era. With a growing number of young chess prodigies emerging from the nation, it is clear that the future of chess is in capable hands.
Gukesh’s Impact: More Than Just a Victory
Gukesh’s win in the World Chess Championship isn’t just a win for him—it’s a victory for the entire chess community and a source of inspiration for aspiring chess players worldwide. His unshakable mental resilience, innovative strategies, and fearless approach to top-level chess have set a new standard for what it means to be a World Champion.
What’s most impressive about Gukesh is his ability to handle the spotlight with grace and humility. In interviews and post-match analysis, he remained grounded and focused on his love for the game, emphasizing that his goal was always to improve, learn, and challenge himself.
Moreover, Gukesh’s rise signals that chess is no longer just about playing for personal glory but also about pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved through the game. He has demonstrated that chess is not just a game of calculation but also a game of imagination, creativity, and daring innovation.
The Tactical Genius of Gukesh
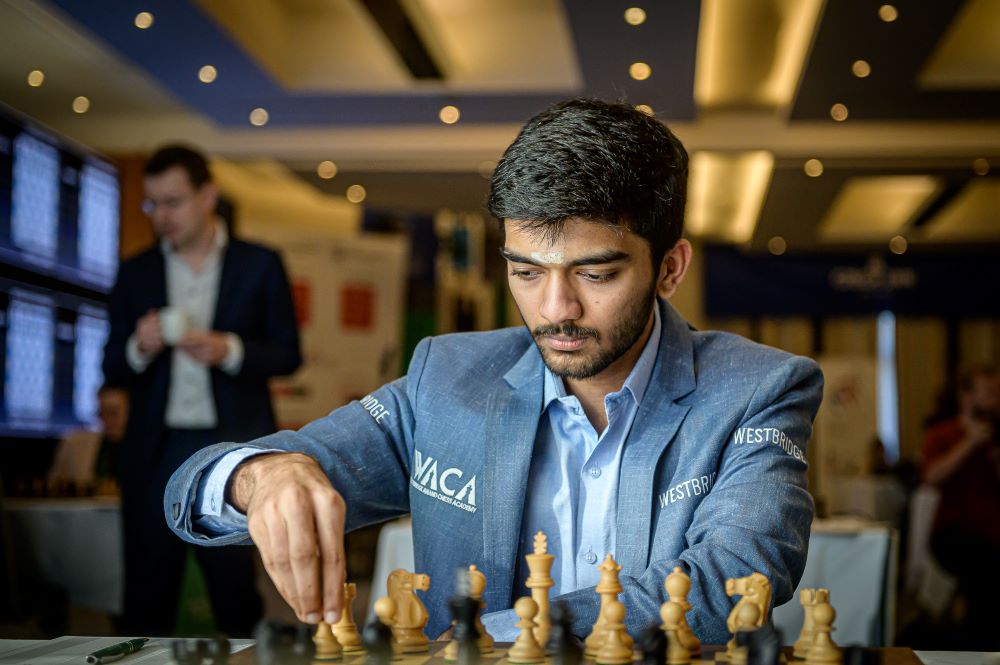

To truly understand Gukesh’s brilliance, one must look at his playstyle. He is not just a player who wins games through well-known lines or memorized tactics. Instead, his genius lies in his ability to create positions that throw his opponents off-balance. Gukesh plays with a deep understanding of dynamics, constantly shifting the balance of power on the board in subtle, unexpected ways.
In his World Chess Championship match, Gukesh deployed some daring openings and unorthodox strategies that kept Carlsen on his toes. The young champion’s readiness to sacrifice material for dynamic play was evident in several crucial moments. His deep knowledge of both classical chess principles and modern innovations gave him the upper hand, making him a multifaceted and unpredictable opponent.
What’s Next for Gukesh?
As the newly crowned World Chess Champion, Gukesh’s future is incredibly bright. With his innovative mindset and unrelenting desire to evolve, Gukesh will continue to push the boundaries of chess. Fans and analysts are already speculating about his potential future achievements, including the possibility of dominating in various formats, from rapid to blitz, and potentially surpassing Carlsen in future world championships.
But for now, Gukesh has earned his moment of glory. His victory at the World Chess Championship will inspire millions of young chess players worldwide, especially in India, where his success has been a beacon for future generations of players.
Conclusion: The Future of Chess is Here
The world of chess has entered a new chapter, and Gukesh D has firmly established himself as one of its most brilliant minds. His remarkable victory at the World Chess Championship is not just the culmination of years of hard work; it’s a reflection of the evolution of chess itself—an evolving game, constantly challenging those who dare to play it at the highest level.
With Gukesh now holding the title, the world watches in anticipation for what’s next. As he continues his journey, it’s clear that we are witnessing the rise of a true chess legend. Gukesh’s victory is not just a win for him; it’s a win for the future of chess.
Reference – Images from google.
For Buy Premium and Quality Chess Click Here – https://bosshandicrafts.com/shop/